1. Damage caused by foreign objects
Damaged compressor wheel or turbine, damaged variable geometry.


2. Lack of lubrication
Wear cracks and material transfer caused by metal-to-metal friction and high temperatures as a result of restrictions in the oil supply. Possible causes include incorrect installation of seals and the use of poor-quality seals or lubricants.

High temperature and material transfer from the bearing.

Incorrect positioning of the seal.
3. Oil contamination
Damage to the bearings caused by high carbon density in the oil, due to extended oil change intervals or poor maintenance. Bearing damage caused by a steel chip suspended in the oil after a major engine repair.

Worn and scratched bearing, material transferred to the shaft.

Large particles in the oil can cause scoring and deep marks.
4. Overspeed and excessive temperature
Turbocharger degradation caused by operating beyond its designed parameters or outside the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications. Maintenance issues, improper engine operation, or unauthorized performance upgrades can push turbocharger speeds beyond their limits, causing fatigue failures of the compressor and turbine wheels.

The orange-peel effect on the back of the compressor wheel is a clear sign of overload.

Turbine wheel with fatigue failure caused by overspeeding.
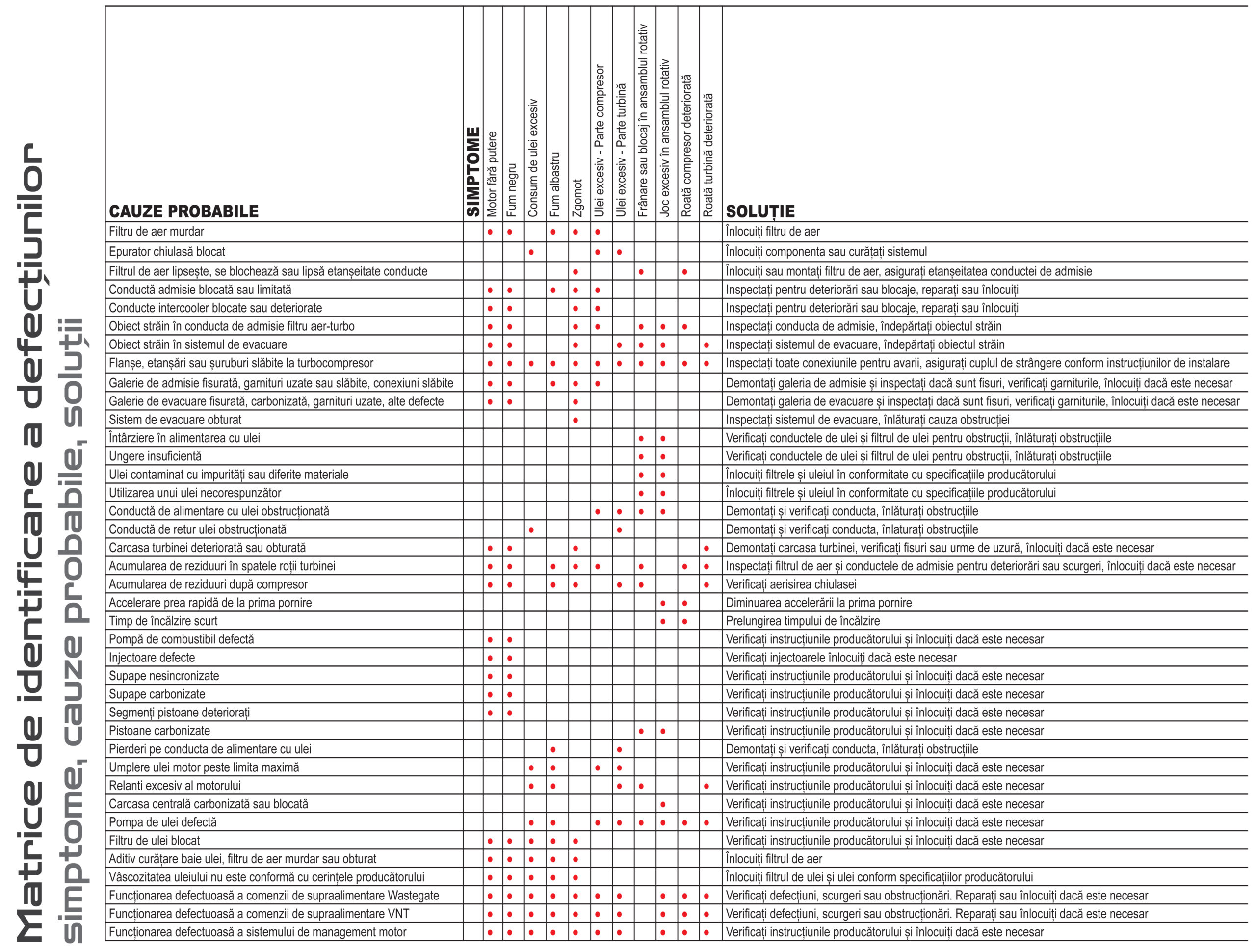
Failure identification matrix